Composr Tutorial: Searching your website
Written by Chris Graham (ocProducts)
As you add content to your website, it becomes increasingly important that your visitors are able to find your content when they need to. Composr includes a 'search' feature, which allows you to search your entire website for content.Simple searching
Detailed searches
The search block for use in panels (different to the search block in the header)
Each kind of content type displays in its own way. For example, matched news posts will look similar to how news looks in the news archive.
Detailed searches
If you would like to carry out detailed searches you need to go to the search module.There are 3 typical ways to reach this:
- By conducting a basic search from the top bar and then changing the options at the bottom of the search results.
- From the search module (site:search page-link, About > Search on the default menus).
- If the search block has been put on a panel then there is a 'More' button there too.
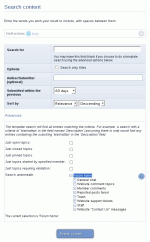
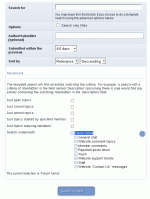
The search module has many options:
Search For
This is the text box where you type the content that you're searching for.Full-text vs Boolean searching
By default full-text searches are used. These are inexact but high performance and more natural. For example a search for "think" would match the word "thinking" or "thinker", and words that are not indexed like "the" would be ignored. Results are returned based on how well they match, so you'll get results that don't match your whole query. Word sequence does not matter unless you use quotes around the words that must be in sequence.You may also do boolean searches which are exact.
Choosing to do a boolean search will make several more options available:
- Content must contain all of these words
- Content must contain one or more of these words
After selecting 'Boolean search', you also gain the several searching possibilities, that you may activate as follows:
- Put speech marks around words that you would like to occur in sequence
- Put a '-' before a word to shun it
- Put a '+' before a word to require it.
Search only titles
With this option checked, Composr will only search titles of content.Author/Submitter
In this field, you can type the name of a member on the website. If you do this, Composr will only look for entries that this person has submitted. It also matches against author names.Submitted within the previous
In this field, you can set a cut-off date, to not show entries that are older.Sort by
In this field, you can specify what order you would like your results shown in.Search the following content types
Placing a checkmark beside each content type will cause Composr to search for entries in these content types. Clearing the checkbox will cause Composr not to search in these locations.Advanced searches
Performing an advanced search for a specific content type
Searching from the Forum
The search button on the forum
User hand-holding
Search autocompletion
When you start typing out a search it can autocomplete. This is based on:- Common past searches
- Matching keywords for the search type
- Matching titles for the search type
All these cases are controlled via privileges (the "Autocomplete searches based on xxx" ones), as potentially it is a leak of private or privileged information. No permissions are checked, so if you grant the privileges then content titles and keywords from private content can potentially leak out.
Did you mean?
If you have spell checking enabled on your server (pspell or enchant PHP extension), then misspellings will result in a suggestion to run a search on an autocorrected search term. Any keyword terms on the site will be considered real words and not autocorrected.Result counts
Unfortunately result counts have to be an approximation. To de-duplicate the result count we'd need to load in the full record sets for each query pattern that runs, which can be incredibly slow, especially if searches are broad.Improving search results
The title fields, and meta keyword fields, get precedence when search results are determined. Tuning these manually for your can improve search results considerably. Additionally keywords are individually queried, rather than having to go through full sentence searching – so you can specify things more precisely, e.g. to include hyphens (which full-text search treats like spaces).If you are using MySQL, also considering turning the MySQL minimum word length down to 3 (the default 4).
Ultimately, full-text search effectiveness resides in MySQL (or whatever database you use), not Composr. For example, indexing does not work on very small words, very common words, and may split things up you did not expect to be (e.g. an-example would split to two words). Also, if there is only one entry in the table, nothing will be returned, because MySQL will only return words that match fewer than 50% of the rows in a table.
True boolean search is much more accurate, but also much slower due to a lack of indexing. Composr will only use true boolean search if boolean search is selected and it thinks MySQL's fulltext-based boolean search won't be able to handle the query itself (e.g. due to using short words). Programmers can alter this logic based on editing the is_under_radar function.
OpenSearch (advanced)
Composr can support OpenSearch, which allows your users to search your website from directly within their web browser. It also supports 'Google Suggest' style search suggestions, based on past searches performed.By default OpenSearch is configured (via the HTML_HEAD.tpl template) to only be active within a zone named docs and for it to only search Comcode pages. You can, however, configure it to perform any search types you like via changing the code used in this template. You should make sure you have a 'favicon' before enabling OpenSearch, as it is important the web browser has one of these available to use.
Slow searches on large sites (advanced)
If you have very large database tables due to very large amounts of content, or having large amounts of content on a multi-language site, you may experience slow-down doing some searches.In fact, the slow-down will cause read locks which prevent writes to those tables. Composr is designed to generally function without database write access, but it's not a good situation to have.
This is a problem that MySQL has with fulltext search. It is not specific to Composr in any way but is worth us documenting.
The problem happens particularly when Composr has to combine the fulltext search with other search constraints.
The inherent technical problem is that if you:
- run the fulltext first – you have to spend a lot of time limiting those hits down to those that match other constraints. The time taken doing this can be extreme if only a small percentage (or even 0%) match your other search constraints, especially for a broad match that has potentially 10's of thousands of fulltext hits – it will basically go on for ever because it never hits a maximum and thus never ends the query.
- run the fulltext last – MySQL can't use the fulltext index effectively, having to throw away large numbers of matches while intersecting against the huge pool of possible rows that matched the other search constraints.
Or in other terms, calculating the intersection between fulltext hits, and other constraints (e.g. forum permissions, or search context) is unindexable and potentially a vast calculation.
This is a serious problem on large databases, but not noticed by most users.
Fortunately we have 3 workarounds.
Workaround 1: Auto-kill slow searches via MySQL scheduler
A workaround is to auto-kill searches that take too long (over 5-10 seconds). It requires server-level MySQL access. That is only a proportion of searches (typically ones with a lot of results, yet none matching the other constraints you are searching against).- Put this into your my.cnf/my.ini file:
Code
event_scheduler=ON - Restart MySQL.
- Run mysql
- Run this query: USE <yourdbname>;
- Run this query:
Code
delimiter |
DROP EVENT IF EXISTS killslowsearches;
CREATE EVENT killslowsearches ON SCHEDULE EVERY 5 SECOND
DO
BEGIN
DECLARE done INT DEFAULT 0;
DECLARE connid INT UNSIGNED;
DECLARE cur1 CURSOR FOR SELECT ID FROM information_schema.PROCESSLIST
WHERE COMMAND = 'Query' AND INFO LIKE '%text_original) AGAINST%' AND TIME >= 5;
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR SQLSTATE '02000' SET done = 1;
OPEN cur1;
REPEAT
FETCH cur1 INTO connid;
IF NOT done THEN
KILL connid;
END IF;
UNTIL done END REPEAT;
CLOSE cur1;
END|
Workaround 2: Auto-kill slow searches via CRON
Create a CRON script like:Code
#!/bin/sh
# Credentials for a MySQL user with PROCESS, SUPER permissions
USERNAME=FILLME
PASSWORD=FILLME
for i in `seq 1 6`;
do
mysql -u $USERNAME --password=$PASSWORD -e 'show processlist\G' |\
egrep -b5 'Time: [0-9]{2,2}' |\
grep 'Id:' |\
cut -d':' -f2 |\
sed 's/^ //' |\
while read id
do
mysql -u $USERNAME --password=$PASSWORD -e "kill $id;"
done
sleep 10
done
This kills any MySQL connections running for more than 2 digits of seconds, including sleeping ones.
Workaround 3: Auto-kill slow searches via MySQL setting
An alternate workaround is possible in MySQL 5.7+, as MySQL have introduced a query timeout setting.Set it in MySQL like:
Code
SET GLOBAL MAX_STATEMENT_TIME=10000;
We actually automatically set this on a session level when you do a search, so there's no need to do anything if you're running MySQL 5.7+.
Workaround 4: Use InnoDB
Another workaround is to switch to InnoDB tables in MySQL 5.6+/MariaDB. It won't stop slow queries, it'll just stop them locking the whole table and slowing other users down; your server will still suffer the load, but so long as your server is not overloaded that is likely not an issue.Feedback
Please rate this tutorial:
Have a suggestion? Report an issue on the tracker.